 Most people have experienced the sensation of having their ears feel temporarily plugged such as after going swimming or being a passenger on an airplane. These sensations are normal and typically disappear almost as quickly as they started. What isn’t normal is when ears feel clogged for longer periods, sometimes days or weeks. Besides the frustration of not being able to hear well, people with clogged ears and their doctors may struggle to determine the cause.
Most people have experienced the sensation of having their ears feel temporarily plugged such as after going swimming or being a passenger on an airplane. These sensations are normal and typically disappear almost as quickly as they started. What isn’t normal is when ears feel clogged for longer periods, sometimes days or weeks. Besides the frustration of not being able to hear well, people with clogged ears and their doctors may struggle to determine the cause.
Sometimes the reason is nothing to worry about, such as the case with impacted earwax. In other cases, the person could have developed an audiological condition such as Meniere’s disease. Below are several common causes behind ears feeling clogged and suggestions for treatments for people who struggle with this often-annoying problem.
The Simplest Reason: Impacted Earwax
The human body naturally produces the sticky substance known as earwax to help rid the ears of dirt and other elements that may end up inside the ear. Earwax normally flushes the intruding substance out of the ear without people even being aware of it. Sometimes the earwax becomes impacted, which means it gets stuck deep within the ear and doesn’t automatically flush itself out. Frequent cleaning of the ears with Q-tips or regular use of earplugs are just two reasons that ears may become impacted with wax.
Here are some typical symptoms of earwax impaction:
- Clogged feeling in the ears
- Coughing
- Difficulty hearing normally
- Earache
- Ear discharge
- Odor coming from the ears
- Ringing sensation in the ears
People who suspect they may have impacted earwax shouldn’t try to dislodge it on their own. Attempting to do so could push the earwax deeper into the ear canal or even cause a ruptured eardrum. Doctors have special earwax cleaning kits that safely flush the ears and return the earwax to its normal functioning. Aside from impacting hearing, impacted earwax may also cause balance issues or cognitive issues.
Up to two-thirds of residents in nursing homes may have impacted earwax, which can worsen hearing loss, falls and cognitive decline https://t.co/1JyETjskIj
— CNN International (@cnni) August 27, 2018
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
A one-time exposure to extremely loud noise such as a blast or ongoing exposure to noises at higher decibels can cause temporary or permanent noise-induced hearing loss. Feeling a sensation of clogged ears is one of the symptoms, and people can also develop ringing in the ears known as tinnitus. The temporary hearing loss usually resolves within 48 hours, but anything longer than that warrants a trip to the audiologist. The best way to prevent this kind of damage is to avoid noisy environments as much as possible or wear earplugs when noise exposure is unavoidable.
Hearing health experts worry that the growing percentages of younger adults suffering from noise-induced hearing loss may be attributable to the rise in usage of earbuds and headphones. Unfortunately, many earbuds users listen to their music at high volumes to drown out surrounding noise. This practice exposes the ears to levels of noise that can cause hearing damage over time.

IQbuds² MAX are a superior alternative to standard earbuds to reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. The earbuds enable listeners to cancel out, augment or blend surrounding noise while streaming music for a better listening experience. This is possible through a combination of Active Noise Cancellation (ANC), directional hearing control (Focus), and Speech in Noise Control (SINC) technology.
Almost anyone with headphones or earbuds likely has cranked up the volume to overpower outside noise at some point. Most have done this without realizing they are potentially damaging their hearing in the process. With ANC technology enabled, IQbuds² MAX users stream music at a much lower volume without being bothered by surrounding noise.
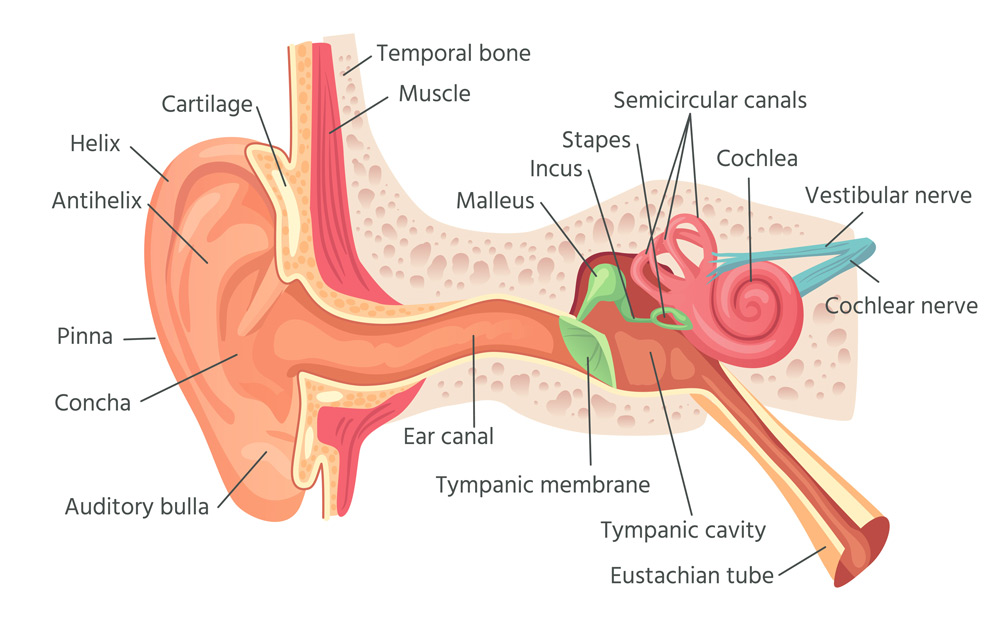
Blockage of the Eustachian Tube
The Eustachian tube connects the throat and the middle ear. Normally, mucus and fluid travel from the middle ear to the back of the throat where people automatically swallow it. When something interrupts this process, the mucus and fluid remain in the middle ear and cause a clogging sensation. Blockage typically occurs due to the common cold, flu, sinusitis, and allergic rhinitis. Coughing, sneezing, sore throat, and runny nose are typical symptoms of a blocked Eustachian tube.
Fluid that remains blocked in the inner ear can lead to an ear infection. This is especially common in young children who don’t have a fully developed Eustachian tube yet. The most prominent symptoms of an ear infection are fever, fatigue, irritability, and pulling at the ears. Ear infections require antibiotics to treat.
Clogged Ears Caused by Sinus Pressure
Sinus pressure can cause both clogged ears and ringing in the ears. People can develop uncomfortable sinus pressure when they have a congested nose and nasal passages due to a cold or allergies. Other causes of sinus pressure include diabetes, bacterial or viral infection, smoking, and swimming. In addition to clogged ears and/or ringing in the ears, people with sinus pressure may experience these symptoms.
- Reduced sense of smell
- Runny nose
- Toothache
- Uncomfortable pressure in the ears, nose, and other areas of the face
Most of the time, the discomfort of sinus pressure goes away on its own within a few days. The problem can sometimes lead to a sinus infection that requires treatment with antibiotics.
Home Remedies for Clogged Ears
One tried-and-true method for unclogging ears is to turn the shower to the hot water setting and inhale the steam for 10 to 15 minutes. This can help to loosen mucus in the ears. Placing a warm washcloth over the ears can also help. Some other simple treatment options include:
- Hold a hairdryer a few inches away from the ears to help dry fluid to allow it to fall out easier.
- Use eardrops periodically to prevent earwax buildup or use a few drops to help loosen wax and mucus in the ears.
- Take an over-the-counter antihistamine or decongestant.
- Try the Valsalva maneuver, which involves pinching the nose while taking a deep breath. The next step is to attempt to exhale gently through the nose with the mouth still closed. A successful Valsalva maneuver should cause the ears to pop as fluid moves away from the Eustachian tube.
If your ear feels clogged, don’t hesitate to contact a doctor when these methods fail to bring relief or they suspect some type of infection.


